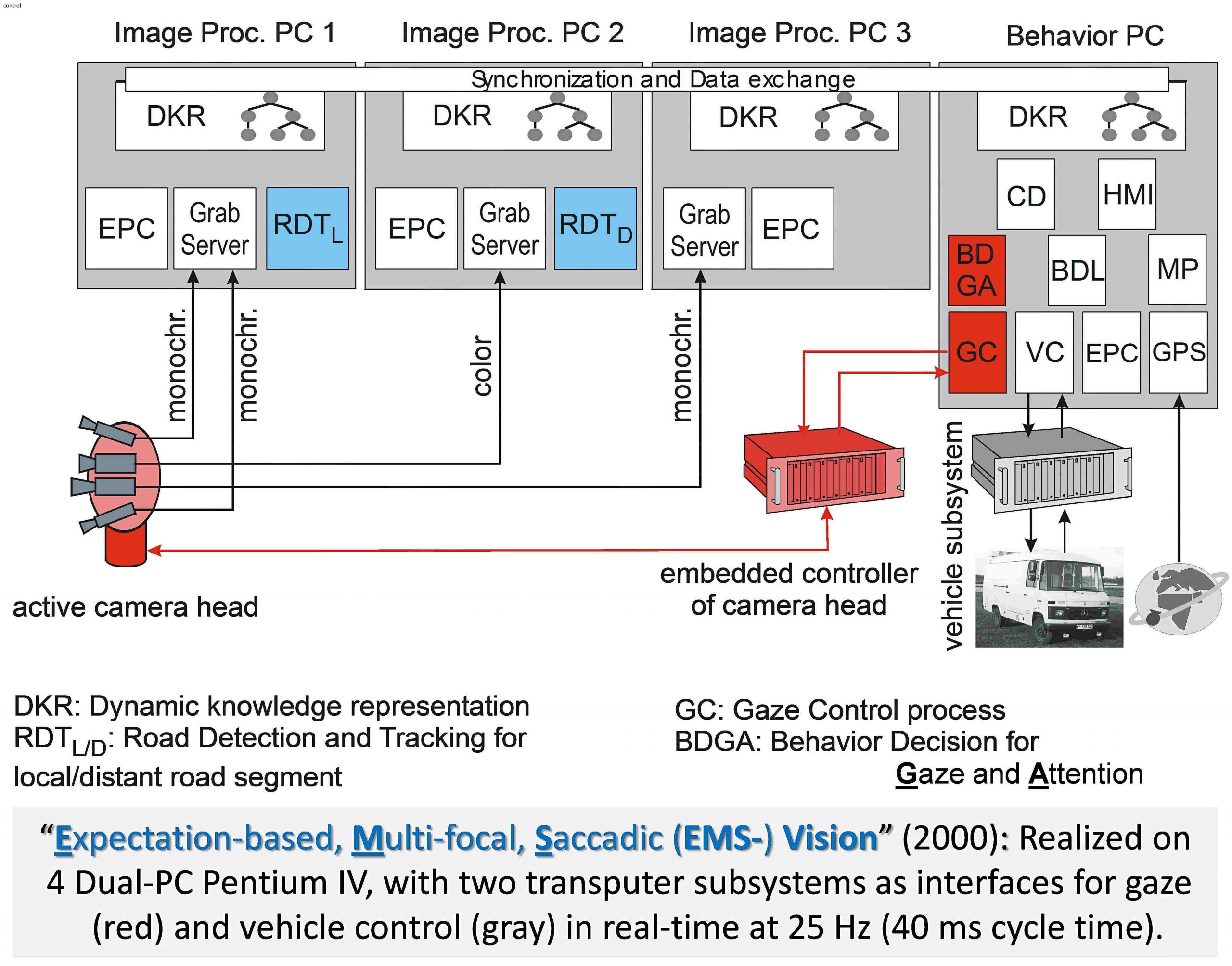
In the late 1990’s, the development of ‘general-purpose-processors’ and high-speed communication networks for PC had reached a state that for the first time allowed full-frame-rate image sequence processing with components right off the shelf. Intel Pentium-class dual-processor PC’s with 0.3 to 1 GHz clock rate have been chosen together with the ‘Scalable Coherent Interface’ – system (SCI) for communication among the PC.
Four Dual-PC Pentium_2, three for image evaluation:
- one for the two divergent wide-angle cameras (b/w);
- one for color camera with mild tele-lens;
- one for highly sensitive b/w-camera with strong tele-lens.
‘Behavior PC’ with the following functions:
- Human Interface (HMI) to all PC in system (EPC),
- High-level Behavior Decision for Mission Performance (CD & MP), for Gaze and Attention (BDGA), and for Locomotion (BDL)
- Interface to the real-time sub-systems for
- Gaze Control (GC, 2-axes platform) and
- Vehicle Control (VC, to all sensors and actuators of the autonomous vehicle)
- Receiving GPS-signals
System integration with COTS-PC:
- Synchronization and data exchange through SCI-network;
- copy of the subsystem for Dynamic Knowledge Representation (DKR) updated on each PC in each cycle.
- Each PC ran independently under the operating system NT to minimize interferences; software-synchronization via temporal models to within a few ms was considered sufficient for the application.
- Hard real-time processing was done with the two subsystems as interfaces to real-world sensors and actuators.
- GPS- frequency of 1 Hz sufficient for navigation.
References
Gregor R, Lützeler M, Pellkofer M, Siedersberger KH, Dickmanns ED (2000). EMS-Vision: A Perceptual System for Autonomous Vehicles. Proc. Int. Symposium on Intelligent Vehicles (IV’2000), Dearborn, (MI). pdf
Maurer M (2000). Knowledge Representation for Flexible Automation of Land Vehicles. Proc. Int. Symp. on Intelligent Vehicles (IV’2000), Dearborn, (MI)
Pellkofer M, Dickmanns ED (2000). EMS-Vision: Gaze Control in Autonomous Vehicles. Proc. Int. Symp. on Intelligent Vehicles (IV’2000), Dearborn, (MI). pdf
Rieder A (2000). Fahrzeuge sehen – Multisensorielle Fahrzeugerkennung in einem verteilten Rechnersystem für autonome Fahrzeuge. Dissertation, UniBwM / LRT. Kurzfassung
Siedersberger KH (2004). Komponenten zur automatischen Fahrzeugführung in sehenden (semi-) autonomen Fahrzeugen. Dissertation, UniBwM / LRT, Kurzfassung